Permcath Placement Vascular Expert Kolkata
Understanding Permcath Placement
Permcath is a type of tunneled dialysis catheter used for patients requiring long-term hemodialysis. It is typically inserted into a large vein, such as the internal jugular vein, and tunneled under the skin to reduce the risk of infection. Permcath placement is a critical procedure often performed by vascular specialists.
Why Permcath Placement is Needed
Patients with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal failure may require hemodialysis for an extended period. Permcath placement is preferred in cases where other forms of vascular access, such as arteriovenous fistulas or grafts, are not feasible or have failed. It serves as a reliable and durable option for long-term dialysis access.
Procedure Overview
Pre-procedure Evaluation:
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, to assess the veins
Permcath Insertion:
- Local anesthesia is administered.
- A small incision is made near the chosen vein.
- The catheter is inserted into the vein and tunneled under the skin.
- The catheter tip is positioned in a large central vein, usually near the heart.
- The other end of the catheter is tunneled and brought out through the skin at a different site to reduce infection risks.
Post-procedure Care:
- Regular monitoring and dressing changes
- Ensuring the catheter remains functional and free from infection
Benefits of Permcath Placement
- Immediate use for dialysis
- Long-term use with proper care
- Lower infection risk due to the tunneled design
- Less invasive compared to other vascular access methods
Risks and Complications
- Infection at the insertion site
- Blood clot formation
- Catheter malfunction or blockage
- Vein damage or bleeding
Seeking Expert Help in Kolkata
Kolkata hosts several renowned vascular experts specializing in Permcath placement. These specialists have extensive experience in vascular access procedures, ensuring the highest standards of care and patient safety.
Top Vascular Experts in Kolkata for Permcath Placement
- Dr. XYZ, MD - A leading vascular surgeon with over 20 years of experience. Affiliated with ABC Hospital, Kolkata. Known for expertise in complex vascular access procedures, including Permcath placement.
- Dr. ABC, MBBS, MS - A prominent vascular specialist at DEF Medical Center. Recognized for innovative techniques and high success rates in Permcath placements.
- Dr. DEF, DM - An expert in interventional radiology, specializing in minimally invasive vascular procedures. Practicing at GHI Hospital, Kolkata.
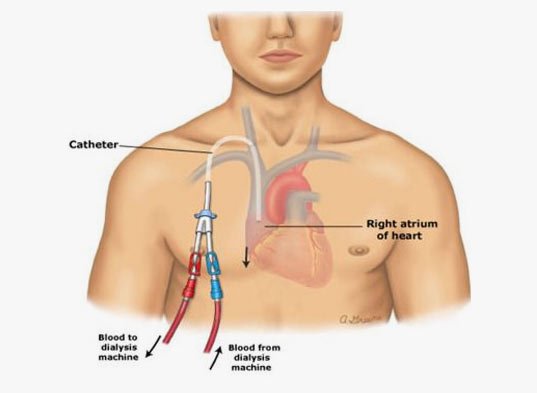
PERMCATH PLACEMENT
A permcath or tunnelled catheter goes into the main vein to which all veins of our hand orleg enters. These cathters are easy to place, easy to handle, lasts for few months to a year and easy to get dialysis done. But kept for long they can cause severe infection and narrowing and can choke the main vein and thereby stop all options of future AV fistula or graft.
Permcath therefore should be used in patients in whom fitula or graft is not possible or has failed or patient needs immediate dialysis and has no fistula.
WHAT IS DVT?
In whom are they common?
They are common in people who had recent history of fever or bedridden state. It is very common after major hip, pelvic, lower limb surgeries. Cancer patients are more prone to Deep vein thrombosis. People who are otherwise active but undergo dehydration can have sudden DVT.

HOW DOES DVT PRESENT?
They may present with sudden onset leg swelling with redness and fever. Pain usually accompanies swelling .
HOW IS IT DIFFERENT FROM CELLULITIS?
Cellulitis is skin and soft tissue infection and can be treated by antibiotics. DVT is clot in major veins and needs to be treated by blood thinners.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE A DVT?
Doppler test is the best modality to diagnose DVT
WHAT ARE THE RISKS OF DVT?
Major DVT s can cause life threatening Pulmonary embolism where a major chunk of the clot can break through and reach the lung vessels and choke them and the patient will stop breathing and collapse and may succumb to death immediately.
The clot in the leg can damage the veins permanently leading to black pigmented swollen legs with recurrent ulcers disfiguring the ankle and feet.


HOW DO YOU TREAT DVT?
An Acute DVT patient should be diagnosed early and treated with blood thinners promptly. In selected patients it is possible to melt or suck the clot using thrombolytic drugs and thrombosuction devices.
CAN PULMONARY EMBOLISM OR DVT BE PREVENTED?
Good hydration, Regular exercise, Abstaining smoking, Seeking preventive care if bedridden or undergoing surgery like using prophylactic medications or stockings can prevent DVT largely.
In a patient with DVT a filter in the main vein of the body can prevent clot to break off and reach lungs thereby preventing life threatening Pulmonary embolism.





Comments
Post a Comment